Search target sum in rotated sorted array
[Arrays]
Problem Statement
Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
(i.e., [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might become [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]).
You are given a target value to find wheater the sum is possible from the array. If found in the array return True, otherwise return False.
You may assume no duplicate exists in the array.
Your algorithm's runtime complexity must be in the order of O(log n).
Example 1:
Input:
- nums = [9, 10, 11, 15, 26, 38]
- target = 35
Output: TrueExample 1:
Input:
- nums = [9, 10, 11, 15, 26, 38]
- target = 45
Output: Falseworks for any input array no matter of reversing and sorting
#collapse-hide
from typing import List
class Solution:
def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
for i in range(len(nums)):
rem = target - nums[i]
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] == rem:
return True
return False
sol = Solution()
sol.search([2, 4, 1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10], 12)
Worst case performance in Time: $O(n^2)$
If the input array is sorted

class Solution:
def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
i = 0
j = len(nums)-1
while(i != j):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
return True
if nums[i] + nums[j] > target:
j -= 1
else:
i += 1
return False
sol = Solution()
sol.search([9, 10, 11, 15, 26, 38], 35)
sol = Solution()
sol.search([9, 10, 11, 15, 26, 38], 45)
If the array is sorted and rotated
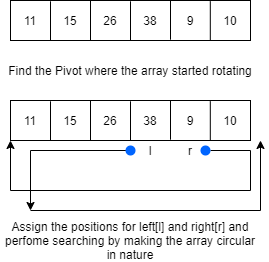
#collapse-hide
class Solution:
def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
l, r = 0, 0
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
if nums[i+1] < nums[i]:
l = i+1
r = i
break
while(l != r):
if l == len(nums)-1:
l = 0
if r == 0:
r = len(nums)-1
if nums[l] + nums[r] == target:
return True
if nums[l] + nums[r] > target:
r -= 1
else:
l += 1
return False
sol = Solution()
sol.search([11, 15, 26, 38, 9, 10], 35)
#collapse-hide
def pairInSorted(arr,s,n):
for i in range(n-1):
if(arr[i]>arr[i+1]):
break
l=(i+1)%n
r=i
while(l!=r):
if(arr[l]+arr[r]==s):
return True
elif(arr[l]+arr[r]>s):
r=(n+r-1)%n
else:
l=(l+1)%n
return False
if __name__=='__main__':
arr=[11, 15, 26, 38, 9, 10]
s=19
print(pairInSorted(arr,s,len(arr)))
Worst case performance in Time: $O(n)$