LinkedList
Sinlgy, Doubly, Circular
- They can be used to implement several other data types:
- Stack
- Queues
- Simple Linked list by themselves do not allow random access tot eh data, so we can not use indexes
- Many basic operations such as obtaining the last node of the list or finding a node that contains a given data or locating the place where a neww node should be inserted - require sequential scanning of most or the list elements.
Advantages
- Linked lists are dynamic data strucutes (arrays are not)
- It can allocate the needed memory in run-time
- very efficient if we want to manipulate the first elements
- can store items with different sizes; an array assumes eveery element to be exactly the same.
- It's easier for a linked list to grow organically. An array's size needs to be known ahead of time, or re-createtd with it needs to grow.
Disadvantages
- Waste memory because of the references
- Nodes in a linkedlist must be read in order from the beginning as linked list have sequential access ( arrays items can be reached via indexes in O(1) time )
- Difficulties arise in linked list when it comes ot reverse traveresing. Singly lined list are extermely diffcult to navigate backwards.
- Solution: Doubly linkked list -> easier to read, but memory is wasted in allocating space ofr a back pointer.
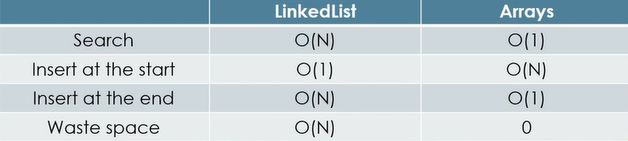
Linked list VS Arrays
-
Search
- Search operation nyieldss the same result for both data structure
- ArrayList search opoearations is pretty fast compared to the linkedlist search operation
- we can use random access iwth arrays:
getitem(int index)which is $O(1)$ time complexity - LinkedList perfomance is $O(N)$ time complexity
- So the conclusion: Arrays list is better for this operation.
-
Deletion
- LinkedList remove operations takes $O(1)$ time if we remove items from the beginning and usually this is the case.
- ArrayList: removing first element (so at the beginning ) takes $O(N)$ tiem, removing the last item takes $O(1)$ times
- But on average: we have to reconstruct the array when reoving
- So the conclusion: LinkedList is better for this operation
-
Memory Management
- Arrays do not need any extra memory
- LinkedList on the other hand do need extra memory because of the references / pointers.
- So in this aspect: arrays are better, they are memory friendly.
class Node:
def __init__(self, info, link=None):
self.info = info
self.link = link
first = Node(10)
print("Node Info:",first.info)
print("Node Link:",first.link)
#collapse-hide
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.size = 0
def insertAtBeginning(self, info):
self.size += 1
newNode = Node(info)
if self.head != None:
newNode.link = self.head
self.head = newNode
else:
self.head = newNode
def insertAtEnd(self, info):
self.size += 1
newNode = Node(info)
if self.head != None:
current = self.head
while current.link != None:
current = current.link
current.link = newNode
else:
self.head = newNode
def insertAtIndex(self, index, info):
newNode = Node(info)
pass
def deleteNode(self, element):
if self.head == None:
print("List empty")
if self.head.info == element:
temp = self.head
self.head = temp.link
temp = None
return
current = self.head
while current.link != None:
if current.link.info == element:
temp = current.link
current.link = temp.link
temp = None
return
current = current.link
print("Element is not found in the list")
def find(self, element):
if self.head == None:
print("List is Empty")
return
current = self.head
while current != None:
if current.info == element:
return True
current = current.link
return False
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current != None:
print(current.info)
current = current.link
def getSize(self):
print(self.size)
def getSizeWcount(self):
size = 0
current = self.head
while current != None:
size += 1
current = current.link
print(size)
ll = LinkedList()
ll.insertAtBeginning(10)
ll.insertAtBeginning(20)
ll.insertAtBeginning(30)
ll.display()
print("****")
ll.insertAtEnd(1)
ll.insertAtEnd(2)
ll.insertAtEnd(3)
ll.display()
ll.getSize()
ll.deleteNode(30)
ll.display()
ll.find(30)
Advantages
- A doubly linked list can be traversesd both directions: forward and backward.
- The remove operation is more efficient if the node is given
For linked list we need the previous node as well. To find it usually we need to traverses the whole list.
- To remvoe a node from singly linked list -> we need the node + Predecessor
- To remove a node from doubly linked lsit -> we need the node .
class Node:
def __init__(self, info, prev=None, next=None):
self.info = info
self.prev = prev
self.next = next
first = Node(10)
print("Node Info:",first.info)
print("Node prev:",first.prev)
print("Node next:",first.next)
#collapse-hide
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insertAtBeginning(self, element):
newNode = Node(element)
if self.head == None:
self.head = newNode
else:
newNode.next = self.head
self.head.prev = newNode
self.head = newNode
def insertAtEnd(self, element):
newNode = Node(element)
if self.head == None:
self.head = newNode
else:
current = self.head
while current.next != None:
current = current.next
current.next = newNode
newNode.prev = current
def deleteNode(self, element):
if self.head == None:
print("Empty List")
# Delete Node in the beginning
if self.head.next == None:
if self.head.info == element:
temp = self.head
self.head = None
temp = None
return
else:
print("Not Found")
# Delete Node in between
temp = self.head.next
while temp.next != None:
if temp.info == element:
temp.prev.next = temp.next
temp.next.prev = temp.prev
temp = None
return
temp = temp.next
# Delete Node in the last
if temp.info == element:
temp.prev.next = None
temp = None
def display(self):
if self.head == None:
print("Empty List")
else:
current = self.head
while current != None:
print(current.info)
current = current.next
dll = LinkedList()
dll.insertAtBeginning(10)
dll.insertAtBeginning(20)
dll.insertAtBeginning(30)
dll.display()
print("*******")
dll.insertAtEnd(1)
dll.insertAtEnd(2)
dll.insertAtEnd(3)
dll.display()
dll.deleteNode(10)
dll.display()
#collapse-hide
import sys
class node:
def __init__(self, info):
self.info = info
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def display(self):
temp = self.head
while (temp):
print( temp.info)
temp = temp.next
def insert_at_beg(self,data):
self.temp = node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = self.temp
return
self.temp.next=self.head
self.head.prev=self.temp
self.head= self.temp
def insert_at_end(self,data):
self.temp = node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = self.temp
return
self.p=self.head
while(self.p.next):
self.p=self.p.next
self.p.next=self.temp
self.temp.prev=self.p
def insert_after_given_node(self,data,item):
self.p=self.head
while self.p is not None:
if(self.p.info==item):
self.temp=node(data)
self.temp.prev=self.p
self.temp.next=self.p.next
if (self.p.next):
self.p.next.prev=self.temp
self.p.next=self.temp
return
self.p=self.p.next
def delete(self,data):
if self.head is None:
print("List is empty")
return
if self.head.next is None:
if self.head.info==data:
self.temp=self.head;
self.head=None
return
else:
print("element not found")
return
if self.head.info==data:
self.temp=self.head
self.head=self.head.next
self.head.prev=None
return
self.temp=self.head
while self.temp.next is not None:
if self.temp.info==data:
self.temp.prev.next=self.temp.next
self.temp.next.prev=self.temp.prev
return
self.temp=self.temp.next
if(self.temp.info==data):
self.temp.prev.next=None;
return
print("element not found")
def reverse(self):
self.p1=self.head
self.p2=self.p1.next
self.p1.next=None
self.p1.prev=self.p2
while self.p2 is not None:
self.p2.prev=self.p2.next
self.p2.next=self.p1
self.p1=self.p2
self.p2=self.p2.prev
self.head=self.p1
print("List reversed\n")
if __name__=='__main__':
llist = LinkedList()
while(1):
print("1.Display\n")
print("2.Insert new node at the beginning\n")
print("3.Insert new node at the end\n")
print("4.Insert new node after the given node\n")
print("5.Delete node\n")
print("6.Reverse list\n")
print("7.Quit\n\n")
print("Enter your choice : ")
choice=int(input())
if(choice==1):
llist.display()
elif(choice==2):
value=int(input())
llist.insert_at_beg(value)
elif(choice==3):
value=int(input())
llist.insert_at_end(value)
elif(choice==4):
print("enter the value")
value=int(input())
print("Enter the element after which to insert : ")
item=int(input())
llist.insert_after_given_node(value,item)
elif(choice==5):
value=int(input())
llist.delete(value)
elif(choice==6):
llist.reverse()
else:
sys.exit(0)
class Node:
def __init__(self, info, next=None):
self.info = info
self.next = None
first = Node(10)
print("Node Info:",first.info)
print("Node next:",first.next)
#collapse-hide
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insertAtBeginning(self, element):
newNode = Node(element)
if self.head == None:
self.head = newNode
self.head.next = self.head
else:
current = self.head
while(current.next != self.head):
current = current.next
current.next = newNode
newNode.next = self.head
self.head = newNode
def insertAtEnd(self, element):
newNode = Node(element)
if self.head == None:
self.head = newNode
self.head.next = self.head
else:
current = self.head
while(current.next != self.head):
current = current.next
current.next = newNode
newNode.next = self.head
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current.next != self.head:
print(current.info)
current = current.next
print(current.info)
csll = LinkedList()
csll.insertAtBeginning(10)
csll.insertAtBeginning(20)
csll.insertAtBeginning(30)
csll.display()
print("*******")
csll.insertAtEnd(1)
csll.insertAtEnd(2)
csll.insertAtEnd(3)
csll.display()